Healthy spine – healthy brain
(This booklet was compiled according to the clinical guidelines of the following organizations: American Academy of Neurology, European Academy of Neurology, American Academy of Family Physicians by our neurologist Mykola Petrenko)
What structure in your body causes pain?
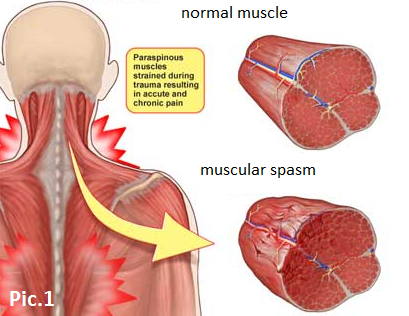
Back pain can result from several causes, but the most common cause is a muscular spasm [1]. There are many small nerves and vessels in muscle tissue that can be mechanically compressed because of a muscle spasm, in this case your body may send you warning signals such as pain. Pic.1
Back muscles tension can be protective. From the evolutionary point of view it protects elastic intervertebral disk from excessive load, but in some cases it can be harmful.
The most common reasons of muscle spasm that can result in back pain
1. Repeated heavy lifting, a sudden awkward movement or staying in the same position for long period of time can strain back muscles and spinal ligaments.
2. Lack of physical activity. Muscles are better supplied with blood during physical activity. Reduced blood flow makes muscles more sensitive to pathological effects.
3. Influence of low temperature, sudden temperature and humidity changes.
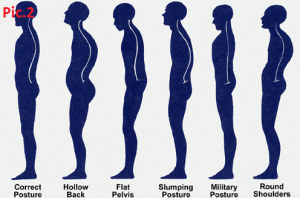
4. Spinal irregularities. Human spine has the S-shaped curvature. This curvature helps the spine act as a shock absorber while still supporting the body’s weight when we move. Unfortunately due to the congenital features many people have spinal irregularities. In this case the load along the back is unevenly distributed and some muscle groups are overloaded. Pic.2
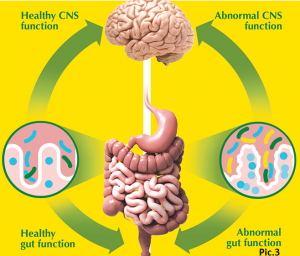
5. Internal diseases. Liver, kidneys, pancreas or intestines can release an excessive amount of harmful substances into the blood if they function abnormally. In this case both muscles and nerve endings become more sensitive to all negative effects. Pic.3
6. Intervertebral disc disease. Intervertebral disks act as shock absorbers between each of the vertebrae in the spinal column. Due to congenital features or due to the lack of necessary substances in nutrition, many people have intervertebral discs that are more sensitive to stress. In this case they may become inflamed, form hernias, which also leads to a muscle spasm and back pain.
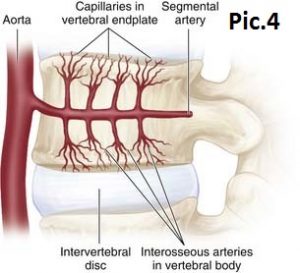
Important! The intervertebral disk itself in most cases cannot be a source of pain, since it normally contains neither nerves nor vessels, and nutrients enter it through diffusion (impregnation). Pic 4.
According to the scientific literature of the last five years, back pain, which has more serious causes than a muscular spasm, is rare. For example, the nerve root compression due to herniated intervertebral disk is observed in less than 10% of cases [2], but nevertheless it is wrongly diagnosed very often. Cases of intervertebral discs "falling out" are completely casuistic, and such "diagnoses" often indicate low qualification of a diagnostician.
If the pain does not go away by itself
If you ignore the back pain for a long time or undergo unqualified treatment, the pain can become chronic.
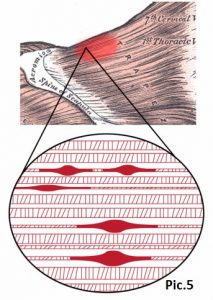
One of the reasons is formation of myofascial trigger points and blocks in the tissue. These are small local muscle indurations, due to which 1) muscles blood supply deteriorates, 2) the brain and the medulla receive signals from these indurations. After a certain period of time the brain begins to perceive them as chronic pain, which has low intensity but can last for years.Pic.5.
Not only pain can be caused by spinal problems
Depending on the localization of the problem, your organism can react to it, generating not only painful sensations.
The persistent increase in muscle tone and the accumulation of trigger points can lead to compression of blood vessels that supply the brain, irritation of the nerves responsible for the functioning of the internal organs, including heart function. Such reactions are very individual and depend on the general condition of your body. Pic.6.
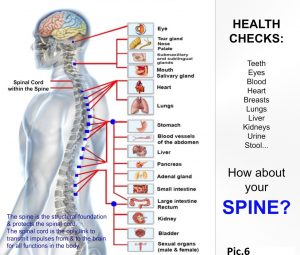
1. Cervical spine problems can cause dizziness, noise in the ears, impaired hands sensitivity, blood pressure disorders, snoring, persistent headache, migraine attacks and a feeling of a lump in the throat.
2. Thoracic spine problem can lead to pain in the heart, respiratory disorders, neurotic disorders, panic attacks.
3. Lumbar spine problem can cause, numbness of legs, pain in joints, night cramps in legs, disruption of the pelvic organons, hemorrhoids, sexual dysfunction.
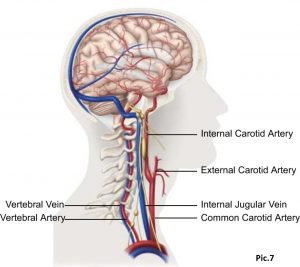
Important! Due to the cervical spine normal state disruption, it is often possible to observe a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Irritability, sleep disturbance, memory loss, depressed mood, loss of motivation are often the first signs in this case. That is why a healthy spine means healthy brain. Pic.7.
How to solve the problem?
Unfortunately, at the moment there are no any magic drugs that would permanently relieve spinal problems. Also, there is no magic “spine cracking” that would heal your spine forever.
If you have spine problems, then you need to understand that your disease is not the result of some kind of one-time negative impact, but has arisen due to a long-term systematic age-related processes and your internal predisposition. The age of the disease onset can be very different and sometimes patient can face the problem before the age of thirty.
Fortunately, taking the right approach, you can get rid of the problem and keep it under control.
The percentage of positive results is much higher than in most other diseases. The main principle of treatment is a systematic impact on your back that will maximize the blood flow along the spine, normalize muscle tone, optimize the flow of nutrients into the muscles, intervertebral discs and nerve structures.
According to the recommendations of American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Neurology and European Academy of Neurology, the first methods, both for acute pain and for the prevention, should be non-pharmacological methods of influence, which include spinal manipulations, reflexology, acupuncture, warming and blood flow enhancing procedures, exercises for spinal muscles stretching [3]. In some cases chondroprotective therapy is recommended [4].
Important! Back exercises should be carefully and individually selected under the guidance of a person who has the appropriate qualifications. Inappropriate exercise selection can exacerbate the problem.
Rational treatment method
The recommended technique includes a complex of reflexotherapeutic procedures aimed to improve the blood supply along the spine that will result in improving the state of the intervertebral discs, deep back muscles and nerves.
1. Manual myofascial therapy.
The procedure is stretching and relaxation of muscles and ligaments using post isometric relaxation techniques and a reflexotherapy massage. The procedure is performed according to clinical studies and recommendations of the German Disease Management Guideline [5].
2. Acupuncture session according to an individual scheme.
Acupuncture session scheme depends on the location and severity of the problem. Disposable sterile needles made of hypoallergenic steel 0.3 mm thick are used. The procedure is usually painless and may be accompanied by a feeling of local distension that is caused by the expansion of small vessels and increased blood flow in the affected area. This method leads to the elimination of trigger points. The procedure is performed according to clinical studies and recommendations of the University Postgraduate Education, Medical University of Vienna, Austria [6].
3. Reflexotherapeutic cupping massage session.
The procedure is not invasive and there is no contact with the patient's blood during the procedure. Vacuum massage is one of the widely studied and promising methods of pain therapy. It is effectively used even for pain caused by cancer. The principle of the method is to enhance the outflow of venous blood, which stimulates the normalization of blood circulation in general. The procedure is performed according to clinical studies and recommendations Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Escola de Enfermagem, Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil [7].
4. Session of pharmacopuncture.
Injections of chondroprotective drugs that improve intervertebral discs and nerves nutrition. Injections are subcutaneous and are performed along the spine using the insulin syringe (length of the needle is up to a centimeter). The procedure is usually painless and has no complications. The procedure is performed according to standard protocol of pharmacopuncture methods.
5. At the end of the session, the patient is given recommendations on the use of personal stretching exercises according to the individual body characteristics. The procedure is performed according to clinical studies and recommendations of American College of Physicians [3].
Full session Duration is about 40-60 minutes.
The recommended course is 3-5-7 procedures, depending on the problem. Performed from one to 3 times a week.
Subjective improvement is noticeable after the first procedure.
Reference list
1. Allegri M, Montella S, Salici F, et al. Mechanisms of low back pain: a guide for diagnosis and therapy. F1000Res. 2016;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-1530. Published 2016 Oct 11. doi:10.12688/f1000research.8105.2
2. Petrenko M. & Svyrydova N (2016). Сучасні аспекти патогенезу, діагностики та лікування болю в спині. EAST EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY .2016 № 4(10) - C. 23-29.
3. Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA; for the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guidlines from the American College of Physicians [published online February 14, 2017]. Ann Intern Med. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
4. B. Danilov, A & V. Grigorenko, N. (2015). An antinociceptive effect of chondroprotectors: A myth or a reality. Zhurnal nevrologii i psikhiatrii im. S.S. Korsakova. 115. 84. 10.17116/jnevro20151159184-89.
5. Chenot JF, Greitemann B, Kladny B, Petzke F, Pfingsten M, Schorr SG. Non-Specific Low Back Pain. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114(51-52):883–890. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2017.0883
6. Lim TK, Ma Y, Berger F, Litscher G. Acupuncture and Neural Mechanism in the Management of Low Back Pain-An Update. Medicines (Basel). 2018;5(3):63. Published 2018 Jun 25. doi:10.3390/medicines5030063
7. Moura CC, Chaves ÉCL, Cardoso ACLR, Nogueira DA, Corrêa HP, Chianca TCM. Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2018;26:e3094. Published 2018 Nov 14. doi:10.1590/1518-8345.2888.3094