Papillomas - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the disease
The skin is the body's protective cloak. The thin, multi-layered cover resists a variety of diseases. It reacts to both external (exogenous) factors and internal (endogenous) troubles. Disruption of the normal functioning of the skin can manifest in numerous symptoms. Sometimes we can observe small formations protruding on the surface of the skin. What is it and what is the reason for it occurrence?
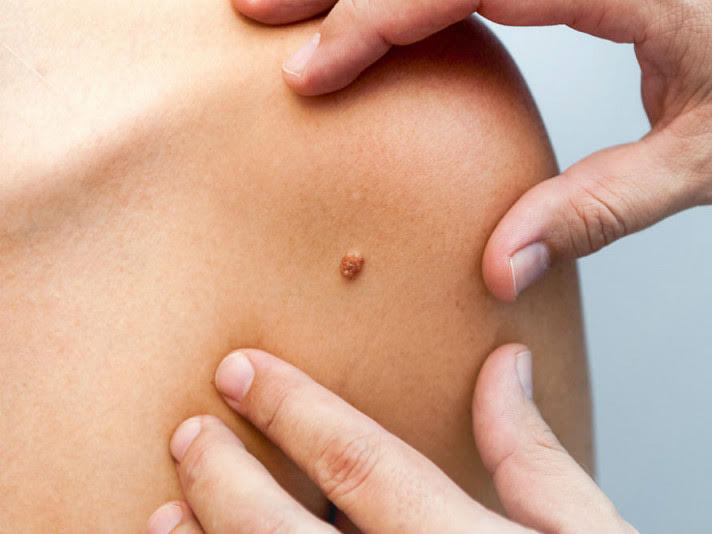
What are papillomas?
Papillomas (warts) - grow on the epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes. Most of these formations are benign and can only cause an aesthetic defect and discomfort when located on traumatic areas.
Why do papillomas occur?
The cause is the human papillomavirus (HPV), a large group of viruses with more than 100 strains. Most of them are not oncogenic, but strains such as 16, 18, and 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52 are the most dangerous in terms of oncological prognosis.
Because of the high number of HPV strains and the possible asymptomatic course, now it is impossible to say what proportion of people are infected with HPV. However, researchers suggest that the figure is considerable and reaches up to 90% of the population.
Several factors can activate HPV and cause clinical manifestations:
- immunodeficiency;
- non-observance of the rules of personal hygiene;
- frequent trauma to a certain area;
- hormonal imbalance;
- the presence of papillomas in relatives is a sign not only of a genetic predisposition, but also simply a factor of close contact and infection with the virus;
- bad habits and others.
Papilloma symptoms
A person can be a carrier of the virus, without even knowing about its existence in the body. Due to the influence of certain external and internal factors, HPV disease begins to manifest on the human skin.
Papillomas are characterized by small, single or multiple skin outgrowths in the form of a bump on a pedicle. They can tend to merge. Often, the color is indistinguishable from normal skin tone. However, it can range from brown to light pink.
They can be mobile when touched. Often these papillomas have a thin stem. These formations are often traumatized and damaged. Sedentary grows have a wide base and are denser in consistency and are resistant to damage.
The location of papillomas can be all over the body and face. However, the most common localizations are:
- armpits;
- eyelids;
- neck;
- genital organs;
- chest area.
These are the most traumatic sites for the skin and frequent damage can induce papillomas to become inflamed and multiply. What's worse, microflora can join the inflammatory process and cause even more discomfort.
Clinical features depend on the type of wart, the most common of which are:
- Common (vulgar) - a common type, especially among children. The clinical signs are small cauliflower growths with numerous papillae on the surface.
- Plantar - can be either single or multiple. Are flat, resemble significant thickening of the skin.
- Flat - multiple and small. Most often located on the face.
HPV genital lesions are quite dangerous. The virus can cause genital warts. Worse, it is the oncogenic effect of HPV that has been proven, and it is the genitals that are often exposed to this effect.
Internal papillomas can cause many problems. By themselves, they often do not have a negative pathogenic effect; however, putting pressure on neighboring structures, they can disrupt their function. Airway obstruction is especially dangerous.
When should you see a doctor?
As we noted, papillomas are benign neoplasms and mostly do not harm the body. However, situations may arise that require a professional assessment of a doctor:
- bleeding;
- constant pain;
- the presence of pus;
- significant cosmetic defect;
- constant trauma to papillomas, for example, as a result of cutting with a razor or rubbing clothes;
- change in color, shape of formations, a progressive increase in their number etc.
Diagnostic methods
Papilloma is a clinical diagnosis. It is diagnosed after examination by a doctor and based on a clinical picture. Additionally, a specialist may prescribe a PCR to determine the type of virus and the level of viral load. To exclude a malignant process, a biopsy is required, followed by pathological verification.
Papilloma treatment methods
In mild cases, the doctor may prescribe the use of skin medications. Nevertheless, the most effective method of treatment is the destruction of the pathological focus in one of the following ways:
- excision - a surgical method of treatment in which the affected area is carved;
- using a laser - a procedure that destroys a wart using high-energy light;
- cryotherapy or tissue freezing with a stream of liquid nitrogen
- electrocoagulation - a point effect on the affected area using an electric current.
We keep repeating that self-medication can be hazardous to health. The use of folk remedies, self-excision, circumcision and shaving of papillomas can lead to the addition of a bacterial infection, an increase in inflammation, and growth of formations.
Disease prevention
Prevention of papillomas is to reduce the risk of infection and clinical manifestations if the virus is already in the body.
You need to follow simple tips:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- rejection of bad habits;
- protected sex;
- HPV vaccination.
Our doctors
In the arsenal of UNIVERSUM.CLINIC, there are specialists who are guided only by modern techniques and the latest protocols. You can get a professional opinion about your papillomas from the following doctors