Lipomas - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the disease
What are lipomas?
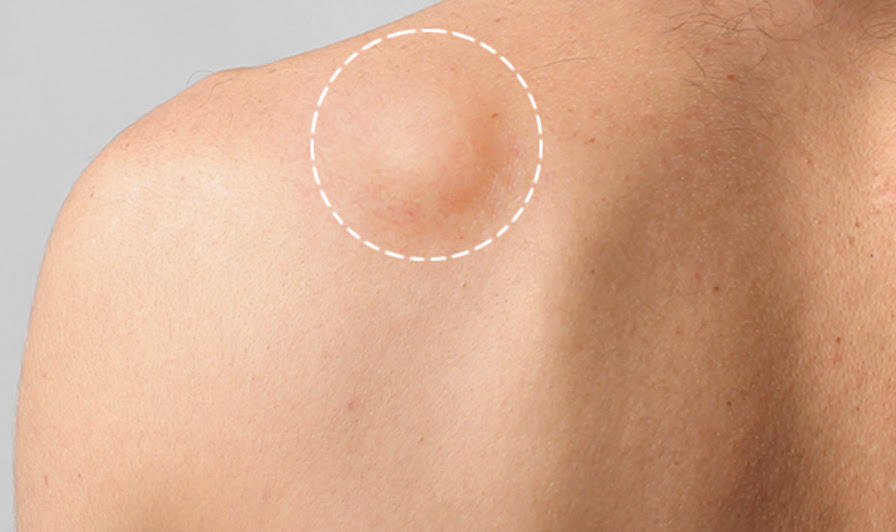
A lipoma is a round or oval formation that grows directly under the skin. It is a piece of adipose tissue that is easily mobile when touched and usually does not cause pain. Lipomas can appear anywhere on the body, but most often they appear on the back, torso, arms, shoulders, and neck.
Lipomas are benign soft tissue formations. They are not cancerous. Most lipomas do not require treatment. If a wen bothers you, your doctor can remove it on an outpatient basis with a one-day surgery.
Why does lipoma occur?
The cause of lipomas is still unknown. There is evidence that the risk of these pineal formations is increased if someone in your family has them. As we can understand, a possible cause is a genetic predisposition. They also occur as a component of syndromes, for example, Cowden, Gardner syndromes, hereditary multiple lipomatosis, and others.
There is a suggestion that the cause is a blockage of the sebaceous glands. Another theory talks about defects in fat metabolism. That is an accumulation of lipids in small vessels, which leads to the formation of a lipoma.
It is worth noting that the formation of wen is more often observed in people aged 40-60 years. This is explained precisely by disorders of lipid metabolism at this age.
Lipoma symptoms
Many people with lipomas are completely asymptomatic. These are usually painless lesions, however, with progressive growth; they can put pressure on adjacent tissues and cause discomfort.
Features of lipomas:
- encapsulated - placed in a capsule and do not spread to surrounding tissues;
- usually solitary, but multiple growth is also possible;
- round or oval shape, symmetrical;
- usually placed directly under the skin;
- movable when touched;
- in the overwhelming majority of cases, they are painless.
Where do lipomas grow?
Lipomas can be diagnosed anywhere in the body. Most lipomas develop directly under the skin on:
- limbs (arms, legs)
- neck;
- back
- near the ears.

Lipomas of internal organs and muscles are a rare.
What are the types of lipomas?
All lipomas are made from fat. However, some also contain vessels or other tissues. There are several types of lipomas, including:
- conventional - the most common, consisting only of white adipose tissue;
- angiolipoma - contain fat and blood vessels, is often painful;
- fibrolipoma - consists not only of fat, but also of connective fibrous tissue;
- hibernoma - differs from conventional lipomas in the type of adipose tissue - here it is brown.
Diagnostic methods
The doctor at the appointment determines the presence and diagnosis of lipoma during the physical examination. The doctor may need a biopsy (taking a piece of tissue) to rule out that it is a malignant neoplasm. For differential diagnosis, that is the exclusion of other similar diseases and confirmation that this is a wen, other additional research methods may be needed. The most commonly used are ultrasound and MRI. It can also help determine the location of the lipoma, the depth of its location. It is extremely important to indicate the blood vessels and whether it presses on nerves or other tissues.
Treatment methods
Most lipomas do not require treatment. If lipoma bothers you or has a significant aesthetic defect, you can seek professional help.
The most effective treatment is surgical removal of the wen. The doctor can perform the procedure on an outpatient basis with the help of one-day surgery. Lipoma removal procedures are safe and effective. You return home the same day.
The surgery is performed under local anesthesia. After the intervention, a small incision heals quickly and leaves almost no scars. Several dressings will need to be done after the operation.
Disease prevention
Can lipomas be prevented?
Many people live with lipomas and they may not even notice them.
Since the predominantly hereditary cause of the appearance of wen is described, it is impossible to prevent them. However, they can be detected at small sizes and removed before lipomas cause significant aesthetic defect and discomfort.
When should I see a doctor?
Millions of people live with lipomas. They can be annoying and unpleasant, but they usually do not cause problems. Most lipomas do not require treatment. Nevertheless, if your lipoma is painful or worried about its size or location, see a specialist.
See your doctor if you notice any changes. The sudden onset of bump pain can be alarming, especially if it tends to grow. You feel the weight of the lipoma, or it does not move so easily when touched.

Our doctors
In the arsenal of UNIVERSUM.CLINIC, there are specialists who are guided only by modern techniques and the latest protocols. You can get a professional opinion about your lipomas from the following doctors: