Phlegmon - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
What is phlegmon?
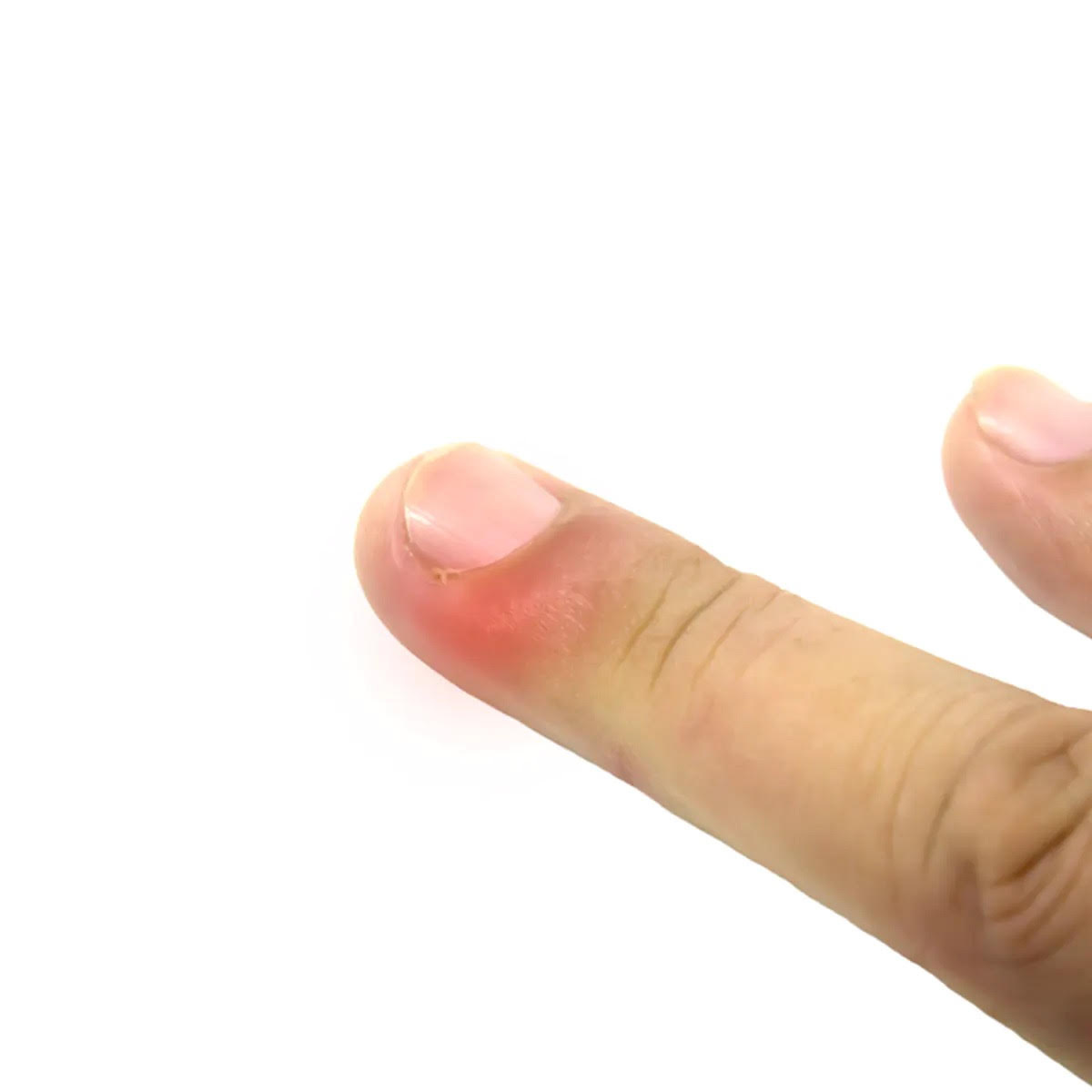

Phlegmon is a purulent inflammatory process characterized by tissue necrosis and the absence of a capsule or boundaries of the lesion. The process spreads to adipose tissue, surrounding muscles and other organs. As the inflammation progresses, it also attracts neighboring structures. It is characterized by the rapid spread of the purulent process, which makes the disease life-threatening.
Why does phlegmon occur?
The condition is caused by bacteria. The most often are group A streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus. The bacteria spread through a scratch, insect or animal bite, or injury, forming a phlegmon just under the skin. An infection of the mouth can cause phlegmon or abscess of the mouth and throat, especially after dental procedures.
Internal organs are also vulnerable; phlegmon does not bypass them. These are usually life-threatening conditions requiring urgent surgery. A striking example is phlegmonous appendicitis.
People with weakened immune systems may be particularly vulnerable to phlegmon, as the response to infection will be less vigorous.
Phlegmon symptoms
The clinical manifestations of phlegmon can be different. It depends on the location, pathogen and extent of the lesion. Delaying treatment is very dangerous, as the disease can be rapidly progressing and lead to irreparable consequences.
Subcutaneous phlegmon is characterized by significant hyperemia (redness), edema, local fever, pain at the site of the lesion.
There may be present systemic signs of a bacterial infection, such as:
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- increased fatigue;
- lack of appetite
- nausea and vomiting
- enlargement and soreness of the lymph nodes and others.

Phlegmon of the neck is often the result of surgical or dental procedures in the mouth and throat. Anatomically, this is a very dangerous location for this disease, since the organ connects the head and trunk and contains numerous cellular spaces. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the purulent process spreads and can cause mediastinitis, encephalitis, meningitis and others.
The feet, legs and hands contain spaces that are also filled with fatty tissue, which is food for bacteria and, accordingly, a substrate for the spread of phlegmon. These are the most traumatic areas, therefore, they require special attention when the first symptoms appear.
Phlegmon does not often affect the face, but such localization is extremely dangerous.
The disease can affect any internal organ. Symptoms vary depending on the organ affected and the specific pathogen. However, phlegmon of internal organs is more difficult to diagnose and it is necessary to pay attention to:
- painful sensations;
- localization of pain;
- violation of organ function.
Diagnostic methods
Superficial phlegmon can be seen with the naked eye. Internal phlegmons are more difficult to diagnose. In the diagnosis of all types, help:
- complete blood count;
- urine analysis;
- ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- MRI, CT - in severe cases.
To distinguish between cellulite (inflammation of adipose tissue), abscess, and phlegmon, your doctor may use gadolinium injections with an MRI to show the outline of the abscess's "wall" versus phlegmon.
The difference between phlegmon and abscess is as follows:
- Phlegmon is unlimited and can continue to spread through connective tissue and muscle fibers.
- The abscess is surrounded by a wall and limited to the area of infection.
- In some cases, it can be difficult to distinguish an abscess from a phlegmon. Sometimes phlegmon occurs when infected material inside an abscess ruptures and spreads.
Read more about the abscess at the link (link).
Treatment methods
Treatment for phlegmon depends on the location and severity of the infection. Typically, treatment includes both antibiotics and surgery.
If skin phlegmon is mild, it can be treated with oral antibiotics. The drug depends on the pathogen. But surgery may be required to clear away the tissue in the area and stop the infection from spreading.
It is important to see a doctor in time for a diagnosis. Phlegmon can be stopped with one-day surgery performed on an outpatient basis. It is highly important to perform surgery as soon as possible to drain the affected area and stop the infection from spreading.
Prevention of phlegmon
Prevention of this disease is the prevention of injuries and damage to the skin, timely treatment of wounds, treatment of such potential sources of infection as caries, pustular skin problems and others.
Our doctors
UNIVERSUM.CLINIC has specialists who are guided only by modern techniques and the latest protocols. For the diagnosis and treatment of phlegmon, you can book an appointment with the following doctors: